As annual ordering cost is inversely related to order size takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
The concept of annual ordering cost and its inverse relationship with order size is a crucial aspect of inventory management. Understanding this relationship enables businesses to optimize their ordering strategies, minimize costs, and enhance operational efficiency.
Factors Affecting Annual Ordering Cost

Annual ordering cost is influenced by several factors, including:
- Order frequency: The number of orders placed over a given period affects the total ordering cost. More frequent orders result in higher ordering costs.
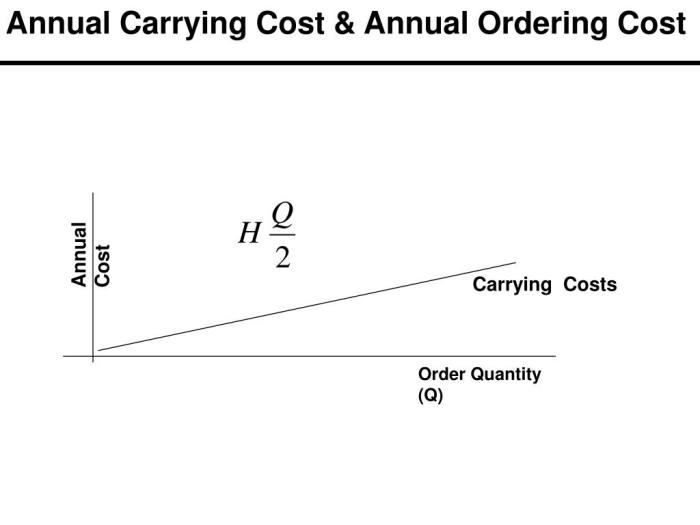
- Inventory holding cost: The cost of holding inventory, including storage, handling, and financing charges, impacts the optimal order size. Higher holding costs lead to smaller order sizes.
- Setup cost: The fixed cost incurred each time an order is placed, such as order processing, shipping, and receiving, influences the optimal order size. Higher setup costs favor larger order sizes.
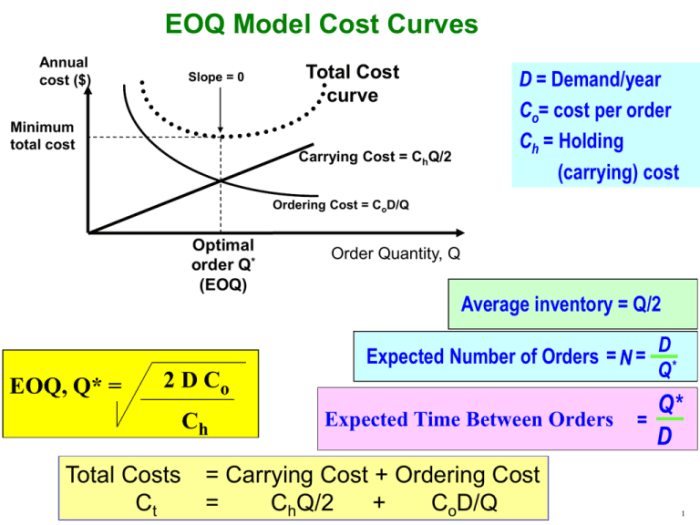
Relationship between Annual Ordering Cost and Order Size, Annual ordering cost is inversely related to order size
The annual ordering cost is inversely related to the order size. This means that as the order size increases, the annual ordering cost decreases. This relationship can be mathematically expressed as:“`AOC = (D/Q)
S
“`where:
- AOC is the annual ordering cost
- D is the annual demand
- Q is the order size
- S is the setup cost
Optimal Order Size
The optimal order size is the quantity that minimizes the annual ordering cost. To determine the optimal order size, businesses can use the following formula:“`Q* = √(2DS/H)“`where:
- Q* is the optimal order size
- D is the annual demand
- S is the setup cost
- H is the inventory holding cost per unit
Case Studies and Examples
Several businesses have successfully implemented strategies to reduce annual ordering cost through optimal order size. For example, a manufacturing company reduced its annual ordering cost by 20% by increasing its order size from 100 units to 200 units. This resulted in a decrease in the number of orders placed and a reduction in the setup cost.
| Order Size | Number of Orders | Setup Cost | Inventory Holding Cost | Annual Ordering Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 units | 10 | $100 | $10 per unit | $1,100 |
| 200 units | 5 | $100 | $10 per unit | $850 |
Quick FAQs: Annual Ordering Cost Is Inversely Related To Order Size
What is annual ordering cost?
Annual ordering cost refers to the fixed costs associated with placing an order, such as order processing, setup costs, and transportation.
How does order size affect annual ordering cost?
Annual ordering cost is inversely related to order size. This means that as order size increases, the number of orders placed decreases, resulting in lower overall ordering costs.
What is the optimal order size?
The optimal order size is the quantity that minimizes the total inventory costs, including annual ordering cost and inventory holding cost.