The Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Unit Test is an essential assessment tool for educators seeking to evaluate students’ understanding of these fundamental geometric concepts. This comprehensive test covers the definitions, properties, relationships, and applications of parallel and perpendicular lines, providing a thorough examination of students’ knowledge and skills.
Throughout the test, students will encounter a variety of questions designed to assess their ability to identify, analyze, and apply their understanding of parallel and perpendicular lines. These questions range from basic definitions to complex problem-solving scenarios, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of students’ mastery of this important topic.
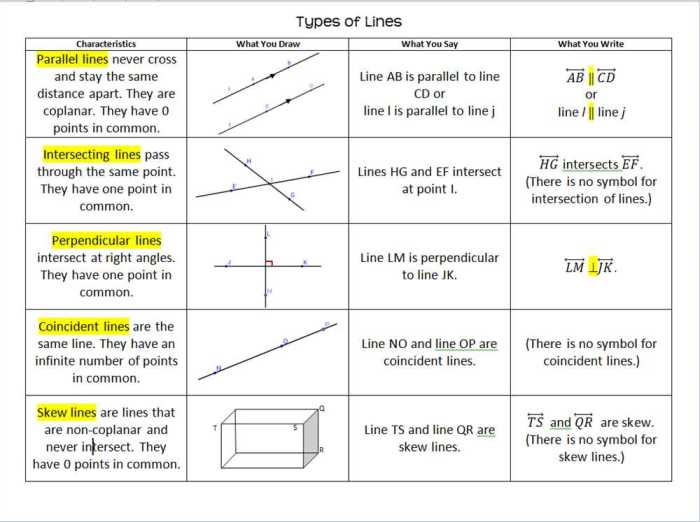
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines: Parallel And Perpendicular Lines Unit Test

Lines in geometry are classified based on their orientation and relationship with each other. Two important types of lines are parallel lines and perpendicular lines, which have distinct properties and applications in various fields.
Definitions
Parallel Lines
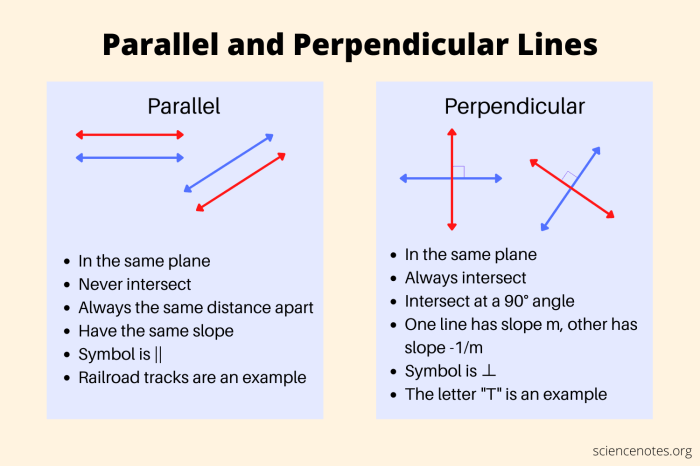
Parallel lines are lines that lie in the same plane and never intersect. They maintain a constant distance from each other as they extend infinitely in both directions.
Perpendicular Lines
Perpendicular lines are lines that intersect at a right angle (90 degrees). They form four right angles when they intersect.
Properties of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
Properties of Parallel Lines
- Parallel lines have the same slope.
- Alternate interior angles formed by a transversal are congruent.
- Corresponding angles formed by a transversal are congruent.
- Same-side interior angles formed by a transversal are supplementary.
Properties of Perpendicular Lines
- Perpendicular lines have slopes that are negative reciprocals of each other.
- Angles formed by perpendicular lines are right angles (90 degrees).
- Segments connecting any two points on perpendicular lines form right triangles.
Relationships Between Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
Parallel and perpendicular lines have a special relationship. If two lines are parallel to a third line, then they are also parallel to each other. Similarly, if two lines are perpendicular to a third line, then they are also perpendicular to each other.
Angle Measures Formed by Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
When parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, the angle measures formed can be categorized as follows:
- Alternate interior angles: congruent
- Corresponding angles: congruent
- Same-side interior angles: supplementary
When perpendicular lines intersect, they form four right angles (90 degrees).
Applications of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines, Parallel and perpendicular lines unit test
Parallel and perpendicular lines have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Architecture: Creating straight lines and angles in buildings, bridges, and other structures.
- Engineering: Designing bridges, roads, and other infrastructure with precise measurements and angles.
- Design: Creating visually appealing and functional products, such as furniture, clothing, and graphic design.
Test Preparation
| Concept | Definition/Property |
|---|---|
| Parallel Lines | – Lines that lie in the same plane and never intersect
|
| Perpendicular Lines | – Lines that intersect at a right angle (90 degrees)
|
| Relationship | – Parallel to a third line: also parallel to each other
Perpendicular to a third line also perpendicular to each other |
| Angle Measures | – Parallel lines: alternate interior and corresponding angles are congruent, same-side interior angles are supplementary
Perpendicular lines form right angles (90 degrees) |
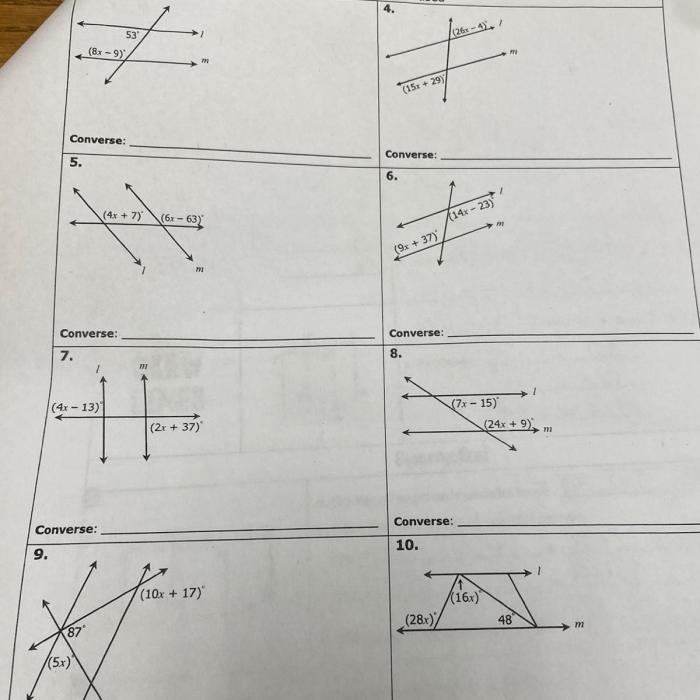
Practice Problems
- Identify whether the lines with equations y = 2x + 1 and y = 2x
3 are parallel, perpendicular, or neither.
- Find the angle measures formed when a transversal intersects two parallel lines with equations y = x and y = x + 2.
- Determine whether the line segment connecting the points (2, 5) and (4, 1) is parallel to or perpendicular to the line segment connecting the points (-1, 2) and (3, 4).
Question & Answer Hub
What is the difference between parallel and perpendicular lines?
Parallel lines are lines that never intersect, while perpendicular lines intersect at a right angle (90 degrees).
What are some real-world applications of parallel and perpendicular lines?
Parallel lines are used in architecture to create structures that are stable and aesthetically pleasing. Perpendicular lines are used in engineering to ensure that structures are built to withstand various forces and loads.
How can I prepare for the Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Unit Test?
Review the definitions, properties, and relationships of parallel and perpendicular lines. Practice solving problems involving these concepts. Utilize online resources and textbooks for additional support.